

This video contains proprietary information and cannot be shared publicly at this time.
Figure 1
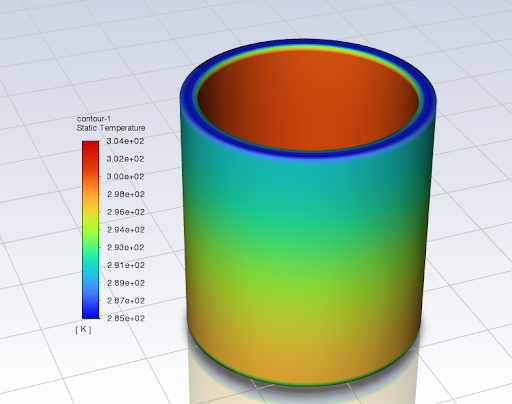
Figure 2
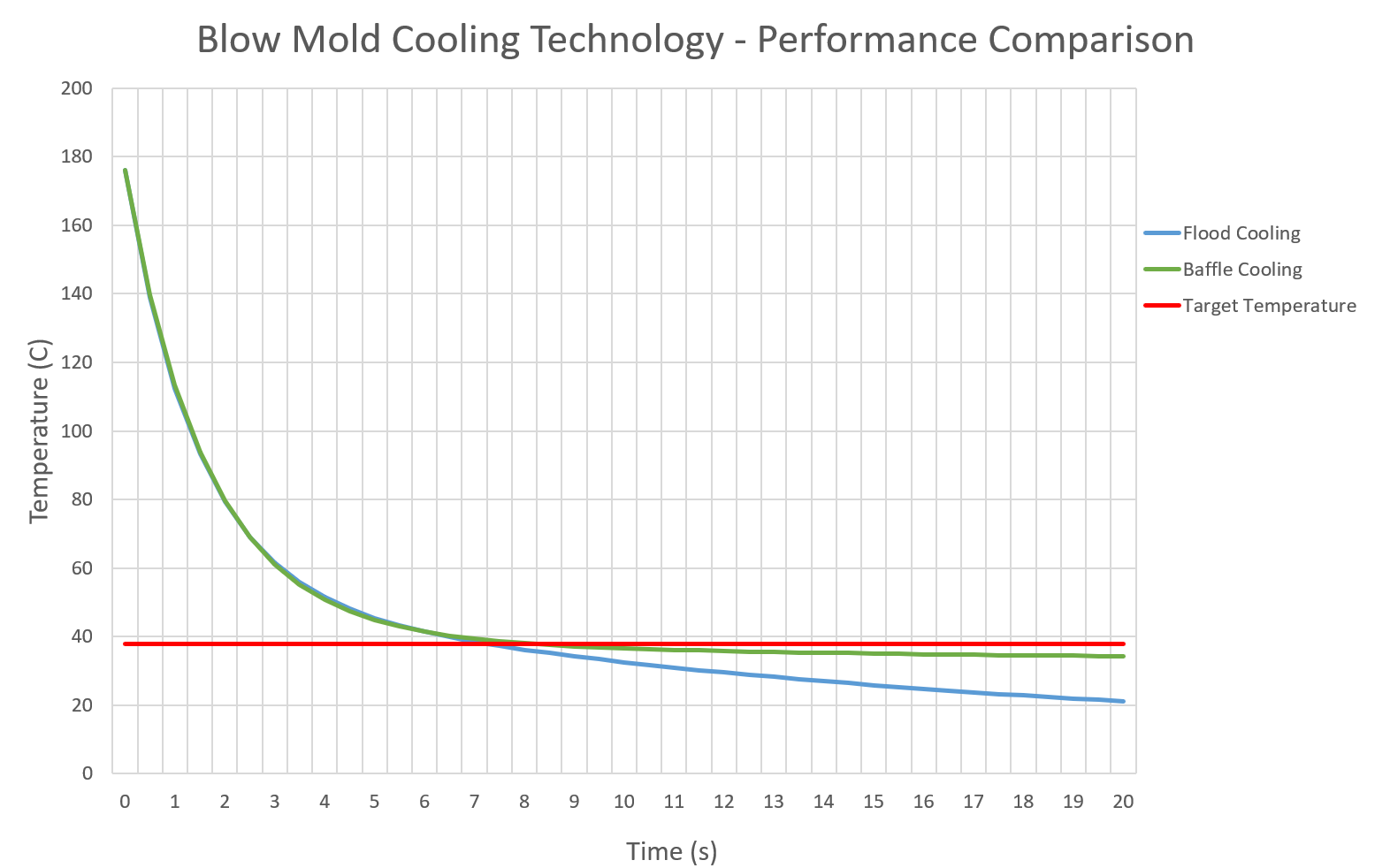
Team 23
Team Members |
Faculty Advisor |
Cory Hemsen |
Professor Jason Lee Sponsor sponsor not indicated by team |
sponsored by

Optimization of Blow Mold Cooling Designs
Heise Industries designs and manufactures extrusion blow-molds. Blow-molding is a manufacturing process for the production of hollow plastic parts. The process of blow-molding is as follows: thermoplastic (called the parison) is heated to its melting point and injected inside the blow-mold cavity, compressed air inflates the molten parison causing it to conform to the shape of the cavity, lastly, the plastic cools and crystallizes before being removed from the mold. Currently, Heise Industries uses a cooling process known as baffle-cooling to cool the hot, inflated plastic. In extrusion blow-molding, the cycle time to make one unit is largely dependent on the amount of time it takes to cool the hot plastic after it has been injected into the mold. The main method of cooling used is convection - cooling water directs heat away from the hot plastic part through cooling channels that are machined into the mold. For companies like the ones interested in buying Heise’s products (i.e., plastic bottle manufacturers), it is advantageous to have a low product cycle time, as this means more bottles can be produced in a shorter period of time. Heise Industries is interested in a new blow-mold cooling technology to improve the cooling rate of their molds and decrease the cycle times they publish to prospective customers. To improve the heat transfer rate of a mold, Heise Industries wants to implement a new method of cooling into their blow mold designs which they refer to as “flood-cooling” technology. These new “flood-cooling” channels increase the surface of the cooling passages compared to conventional designs. Team ME23’s objective has been to design and analyze an extrusion blow mold with flood-cooling technology for Heise Industries to compare its performance to conventional designs.
