
Figure 1
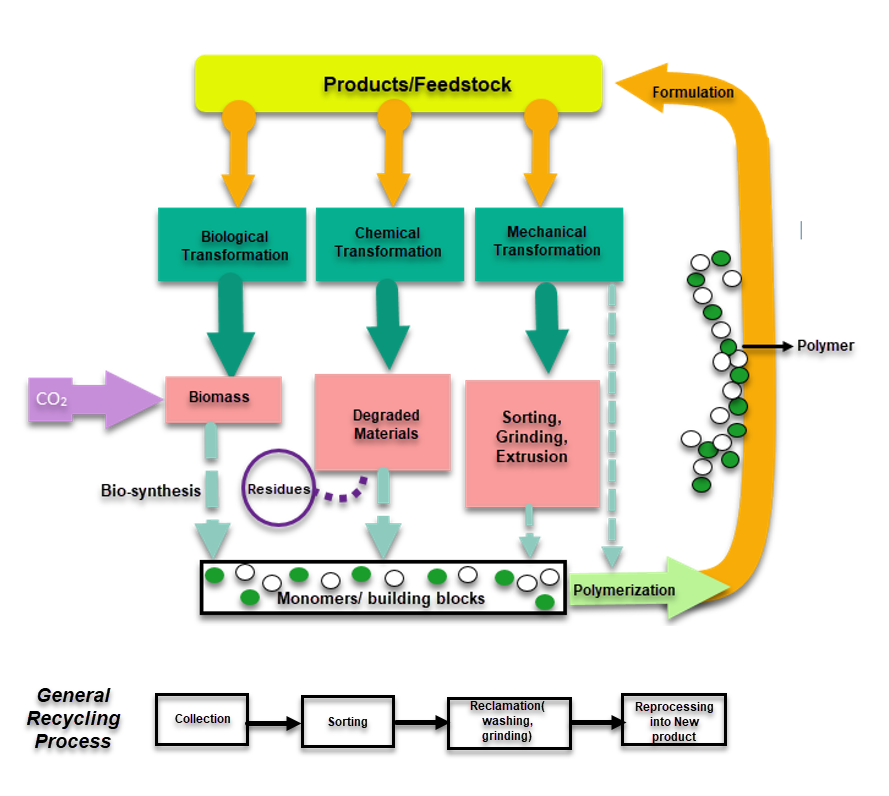
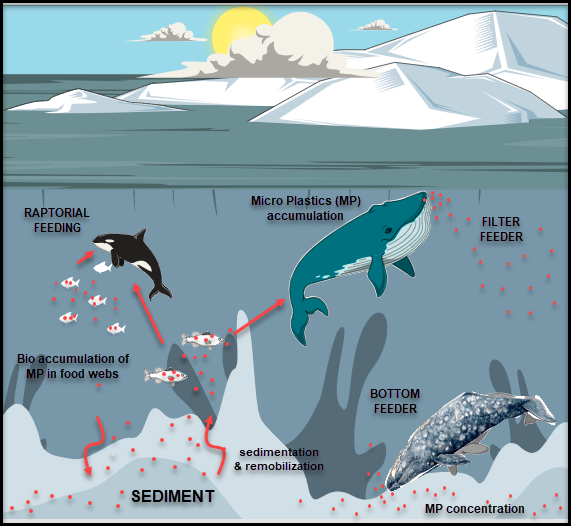
Figure 2
Team 18
Team Members |
Faculty Advisor |
Nour Hashem |
Luyi Sun Sponsor University of Connecticut |
sponsored by
Sponsor Image Not Available
Sustainable Plastics for a More Sustainable World
In recent years, the scale of the plastic pollution crisis has come to light along with the negative impacts it has on our planet. The goal of this project is to not only determine an effective alternative to modern day plastics, but also to better understand methods of disposal and re-use to decrease the damage being done to the environment. Plastics used around the world today have been designed to not break down over time and therefore remain in the environment after their use. By using alternatives such as Polylactic Acid (PLA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL), the degradation process can occur much quicker than traditional plastics, and recycling can become more effective. The process of degradation in these plastics eliminates the issue of microplastics which are much more difficult to collect than other plastic waste as they can spread much further into waterways and oceans. Another key aspect of the degradation process is that it is possible to stop degradation at a certain point, to not completely degrade, to allow for upcycling, creating a more valuable product from discarded materials. Recyclable plastics reduce the need for manufacturing of new plastics, consequently reducing carbon dioxide emissions in the plastic industry. While carbon emissions are separate from the plastic pollution crisis, mitigating pollution of all kinds is important when considering sustainability of plastics. For these bioplastics to replace traditional plastics effectively, improved composting and recycling technology must be developed along with preventative measures to keep pollutants out of waterways. On top of technological advancements, governments must begin to act, like what is being done in terms of carbon emissions. By switching to biodegradable plastics and focusing on proper disposal, the negative impacts of the plastic industry can be reduced in the environment allowing nature to heal and marine life to thrive once again in our oceans.
